Flipkart Grid 2.0
National Finalists of Flipkart Grid 2.0!!!!

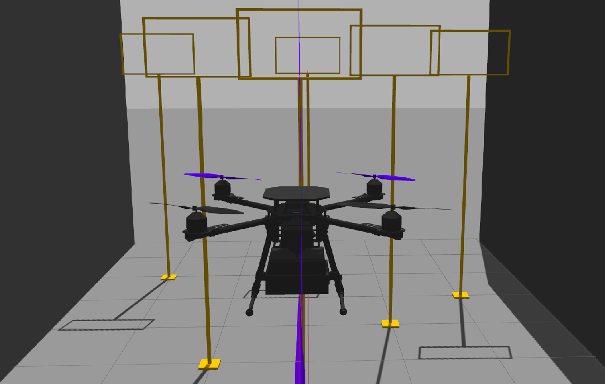
Autonomous Indoor Drone

Abstract
Drones have recently garnered a lot of attention in all sorts of domains including supply chain. While autonomous drones have achieved decent maturity in outdoor environments, the conventional drones still struggle to perform in an indoor environment such as a warehouse. The main reason for this comes from the fact that in outdoor environments, drones could rely on global navigation systems such as GPS for their position and velocity estimates. However when it comes to an indoor environment there is a lot of scope of innovation of sensors and processing.
Problem Statement:
Objective
- The objective of the problem statement is to come up with an autonomous drone which is capable to travel along a predefined trajectory
- The drone should be able to course correct the trajectory to be able to achieve objectives such as crossing through some square frames (gate) or avoiding obstacles in its path
- Parameters :
- Multi-rotor drone
- Minimum payload : 2 Kg
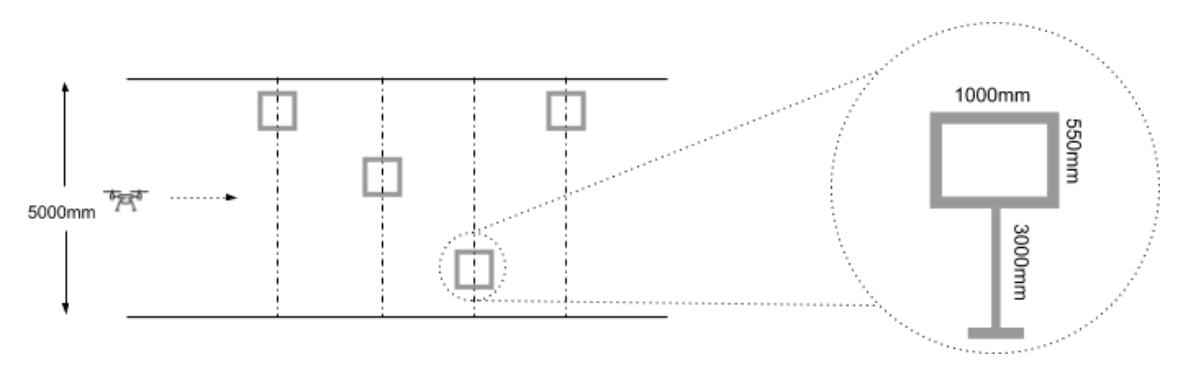
- Navigate in the aisle width of 5000mm
- Autopilot, PID controlled & obstacle avoidance features
Trajectory Specification:
- The drone will travel along a straight aisle.
- The aisle will have 15 gates which the drone has to pass through.
- The gates can be placed anywhere in the aisle but will stay perpendicular to the aisle.
Gate Specification:
- The gate will be a rectangular frame 550 x 1000 mm ( L x B )
- The gate will be mounted on a frame at the height of 3000mm
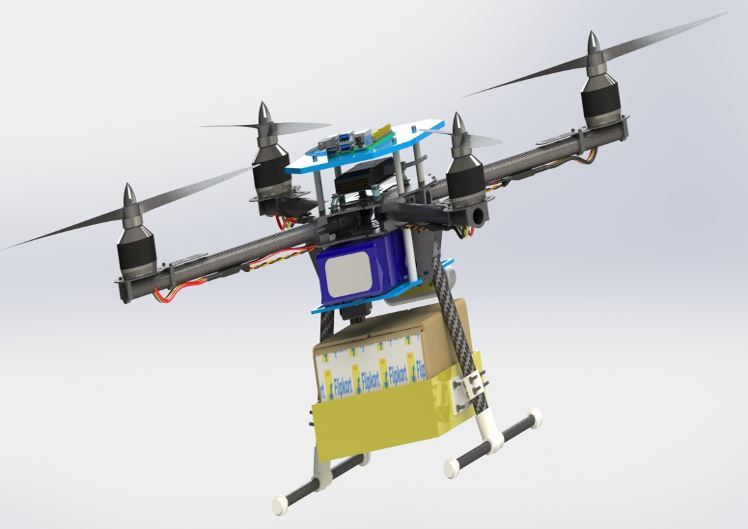
My primary contribution lies here. I was responsible for designing the frame and performing structural as well as Dynamic analysis.
CAD is designed in SolidWorks and Analysis was done in Ansys.
A strong and sturdy carbon-fibre frame is chosen which is well capable of handling the stresses encountered during the mission The Centre of Mass lies below the plane of rotors. This provides inherent stability to the quadrotor. Being a uniform gravity environment, the quadrotor is an inherently Neutrally Stable System. The flight control algorithm ensures further stability of the system.
CAD is designed in SolidWorks and Analysis was done in Ansys.
A strong and sturdy carbon-fibre frame is chosen which is well capable of handling the stresses encountered during the mission The Centre of Mass lies below the plane of rotors. This provides inherent stability to the quadrotor. Being a uniform gravity environment, the quadrotor is an inherently Neutrally Stable System. The flight control algorithm ensures further stability of the system.

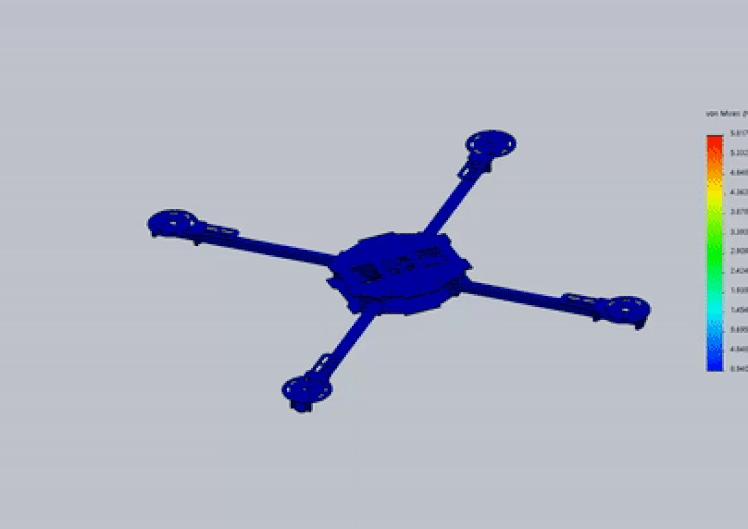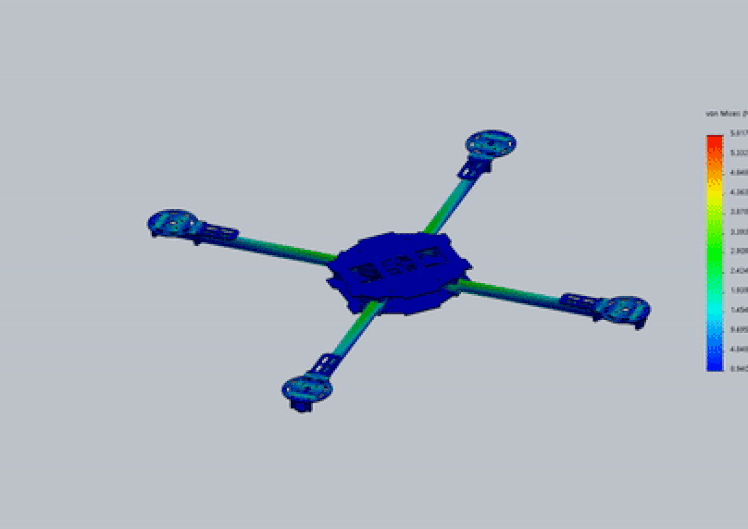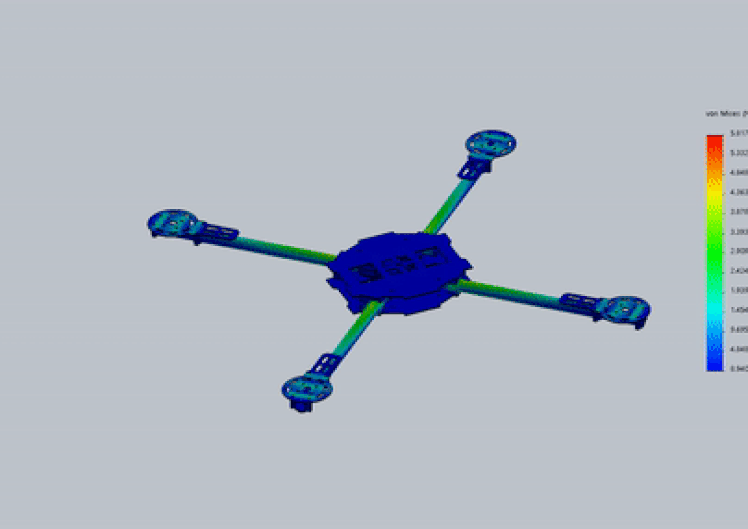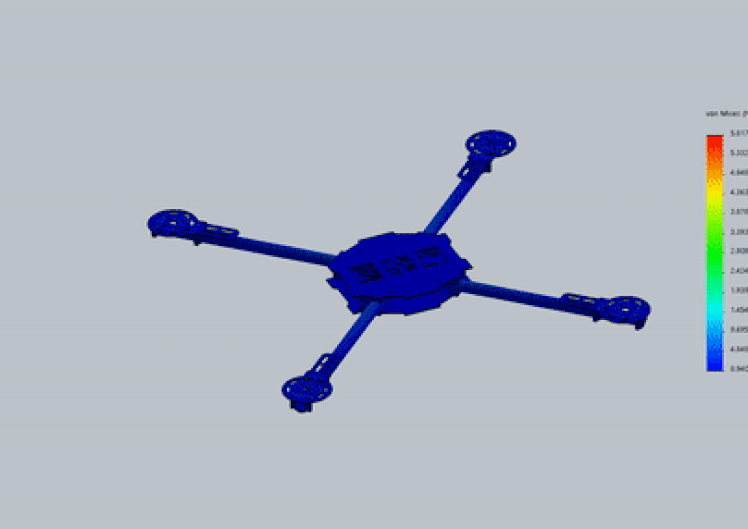
structure Analysis
Material : Thornel MAT VMA (carbon fiber), maximum stress capability : 1.4e+09 Pa (N/m2)Analysis: Based on Von Mises yield criteria
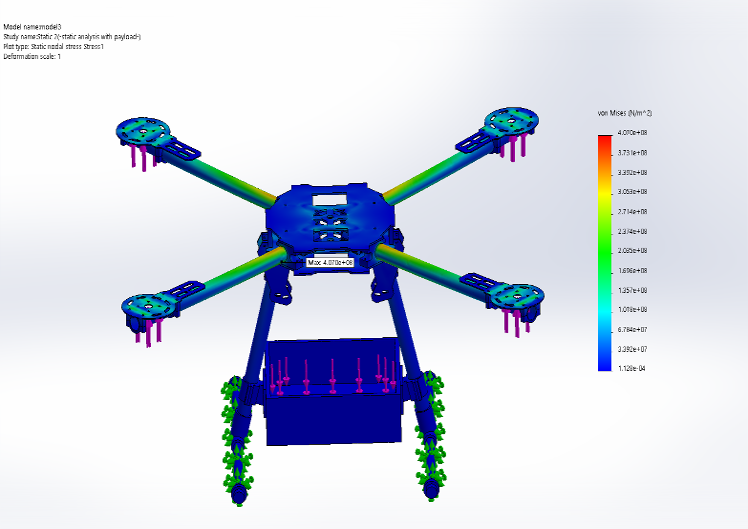
With Payload
- Maximum stress on arms of model during flight is : 4.07e+08 Pa (N/m2)
- Material’s yield stress is 3.4 the maximum stress experienced by it, hence frame will sustain
Without Payload
- Maximum stress on arms of model during flight is : 4.019e+08 Pa (N/m2)
- Material’s yield stress is 3.5 the maximum stress experienced by it, hence frame will sustain
Modal (Vibration) Analysis
Variation of displacement amplitude with different exciting frequencies for our quadrotor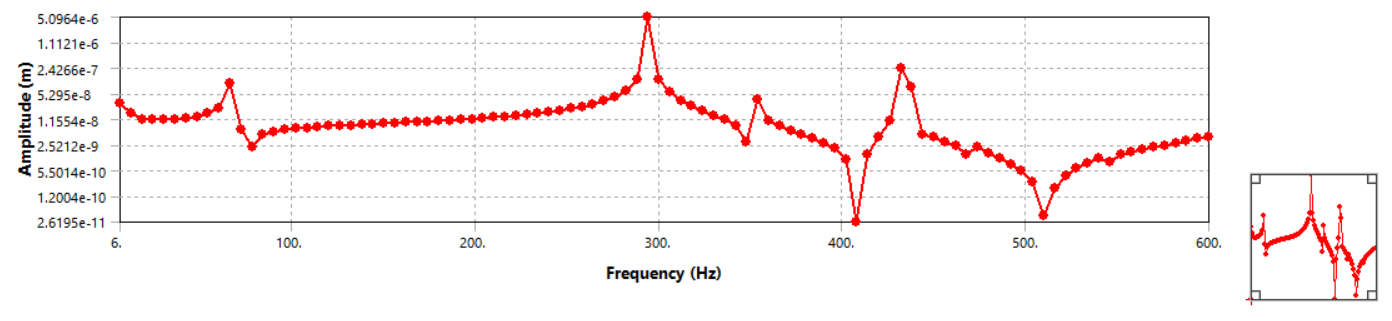
We are using PX4 Software-In-The-Loop
(SITL), which is a very important tool to model the behaviour of the quadrotor in a simulated world.
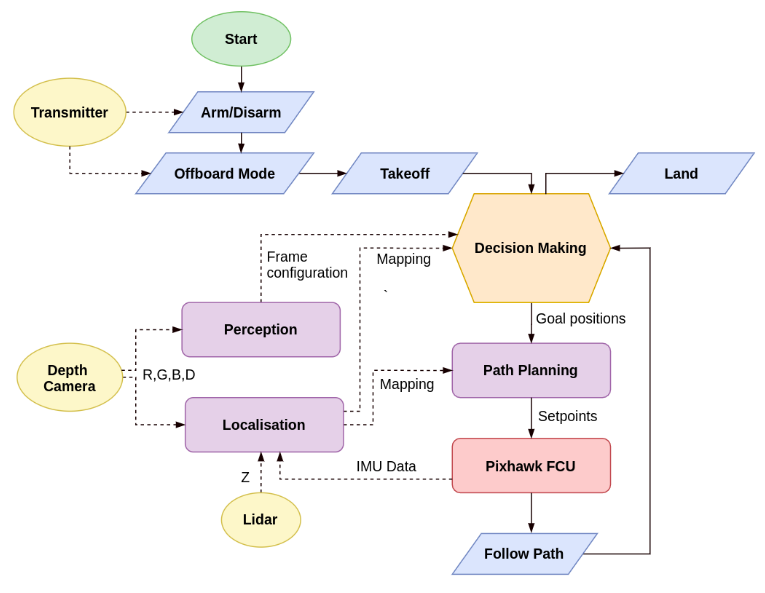
Decision Making:

- Perception node maintains a python dictionary of positions of all the 15 frames
- If the quadrotor has passed through i th frame, and the location of i+1 th frame is still unknown, then it begins to perform a left-right search manoeuvre
- If the position of i+1 th frame is known, then the path planning node generates a optimal path avoiding all obstacles
- This path is fed to the FCU via the rostopic /mavros/setpoint_raw/position
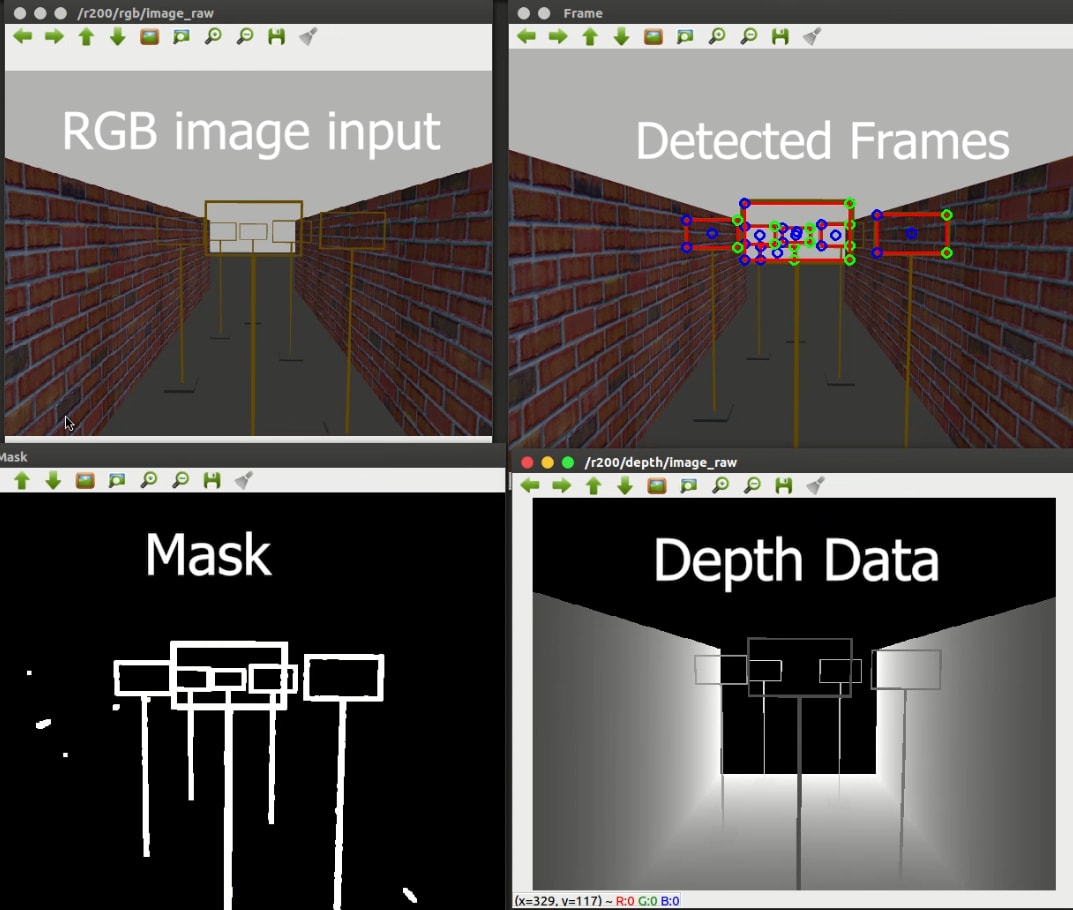
Frame Detection
camera feed in the bottom right.
The frame detection algorithm first detects the corners and then applies matrix transformations to obtain the locations of the frames.
The depth camera feed is used to correctly distinguish between frames that appear to be intersecting.
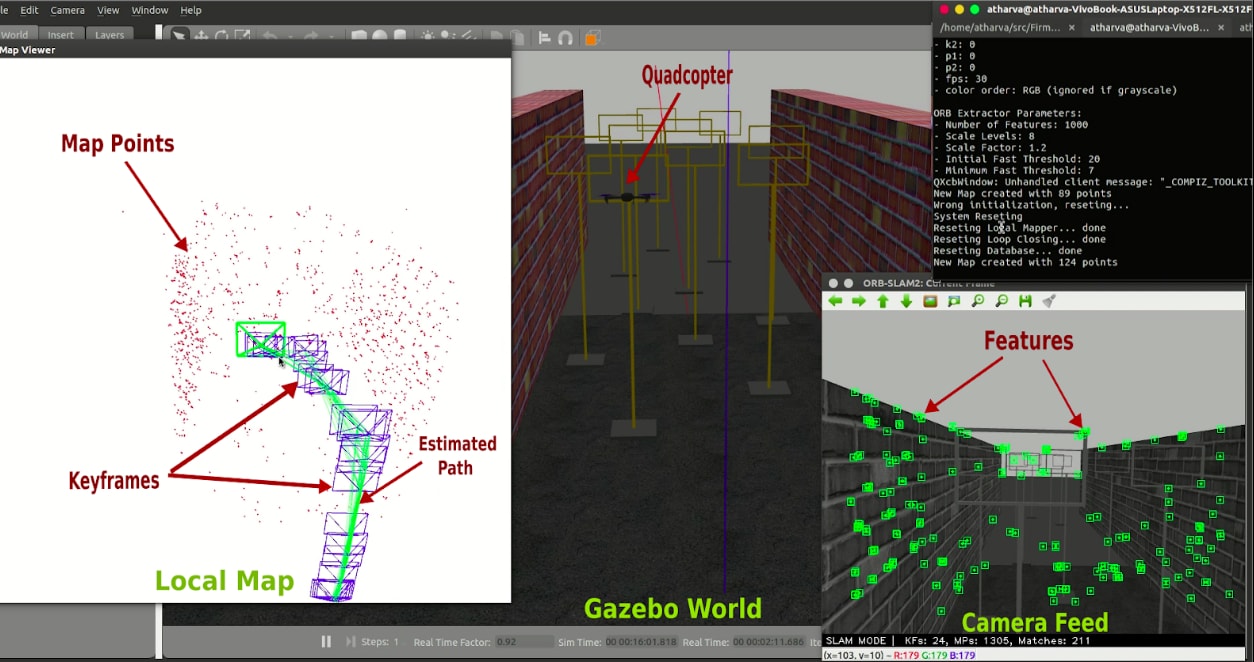
Localisation
ORBSLAM2 is being used for localisation.It extracts key features form the environment and fuses their relative variation with the IMU data to estimate the pose. The arrow in the point cloud shows the estimated position and orientation of the quadrotor.
The top right terminal is showing actual pose by mavros and bottom right is pose measured by integrating SLAM and lidar. We see that they are nearly equal.